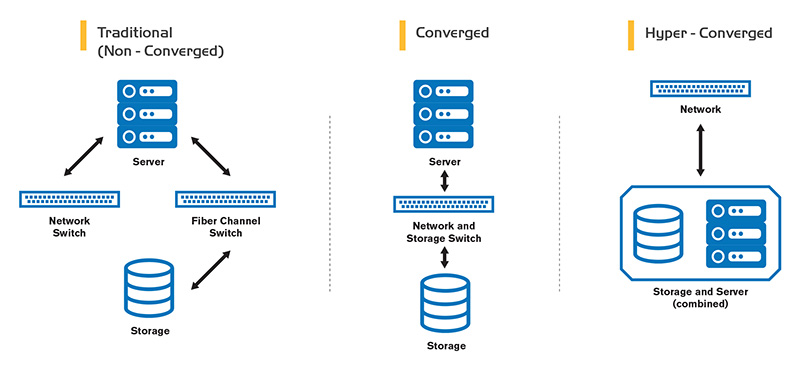
Traditional Infrastructure
Traditional Infrastructure typically includes [insert stack items: server, switches, etc]. This hardware is expensive and bulky, taking up large amounts of power and labor. Servers, networking, and storage each have to be managed by their own experts. The setups are not easily scalable – building out additional VMs as the company grew was a complex task as servers, networking and storage had to all work together stalling the company’s ability to conquer new ventures. If the company was planning to grow they would have to forecast the amount of server and storage they would need for the next 3-5 years.
Converged Infrastructure
Converged Infrastructure eliminates the dedicated SAN-based storage into a single appliance. This offers simplified management, faster deployment, and lower acquisition cost. Although converged systems were a step in the right direction they did not solve all data management issues, the system only includes the server and storage components, and resource ratios (CPU:storage:network) are fixed making this less flexible than what most companies need.
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure natively integrates compute and storage into a single server. This eliminates the bulk of legacy standalone hypervisors and storage complexity; while reducing power and space. Hyper-Converged offers many strengths that are not available in legacy infrastructures including:
- Data Protection
- Deduplication
- WAN (Wide-Area Network) Optimization
- Solid-State Drive (SSD) Arrays
- Public Cloud Gateways
- Automation
- Analytics
- Self-Healing